PV168
Testing
Why test?
- Does it make sense to test your code?
- Related to UX, nobody likes buggy software
- Related to your team, nobody likes to change untested software
- Your future self will thank you
Testing
- Similar to sience
- We have some assumptions about our code
- We try to prove them
- We investigate discrepancies and anomalies
How to properly test?
- Jurassic Park testing
- don’t think about yourself as perfectionst
- you can make mistake and you can’t know everything
- complex systems will fail
- tests are not just some confirmation you MUST have
Few testing methods - Boundary values
- Just below nominal value
- Nominal value
- Just above nominal value
- MIN and MAX
Equivalence Partitiong
- dividing input data in data classes
- for password input 4 - 10 characters
- (1..3), (4..10), (10..MAX)
Use-case testing
- use real data examples
- imitate user actions
- happy path
Decision table
- many conditions, rules control

State transition
- STATUS - many options
- ACTION - change trigger
- TRANSITION - from one state to other
- test every status, every action, every transition -> every path
Pairwise testing

Pairwise testing

https://eviltester.github.io/TestingApp/apps/7charval/simple7charvalidation.htm
Test Categories
- End-To-End Tests
- User behaviour simulation (full application stack)
- Hard to automate, slow, costly maintenance
- Integration Tests
- Testing interoperability of components
- Faster and less complex than full-stack tests
- Unit Tests
- Testing components in isolation
- Super-fast and easy result interpretation
Black-box vs White-box Testing
- Black-box Testing
- Only using public API of Unit/Component (without seeing the internals)
- Concentrating on scenarios (implementation details are irrelevant)
- Default option (for new code)
- White-box Testing
- Test-cases are driven by the internals of Unit/Component
- Enforces internal data structures and design
Testing ice cream cone

Testing Pyramid

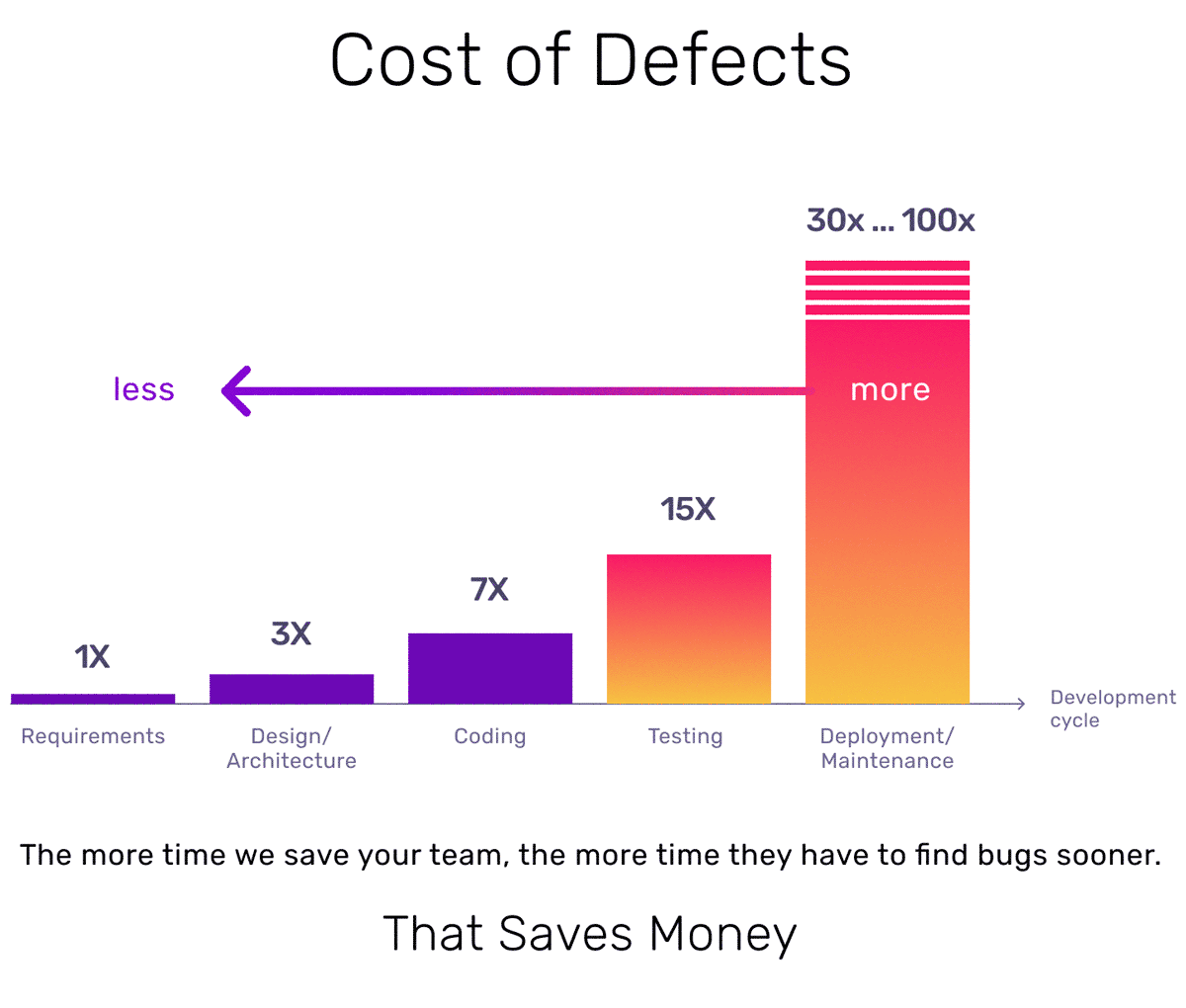
Why Unit test?
- The cost of the bug raise exponentially with time
Code Coverage
- Percentage of production code covered with tests
- Ideally close to 100%
- Might be difficult to achieve
- Demanding particular coverage (e.g. 80%) leads to problems
- Cheating with poor tests to fulfill metrics
- Even 100% coverage may not be enough
- Quantity cannot trump quality
When to Write a Test
- Test-first development
- Write code after writing Unit/Integration tests
- Leads to loosely-coupled, reusable and testable code
- Ideally follow TDD
- Test-last (if ever) development
- Write all the code, then (maybe) some tests
- Unfortunately still very common in the industry (school-style)
- Leads to compact, highly-cohesive, hard-to-test code
Test Anatomy
- Given (Arrange)
- When (Act)
- Certain action is performed
- Then (Assert)
Test Isolation
- Tests don’t interfere with each other
- Each test responsible for Setup and Teardown
- Share only stateless and expensive resources
- Higher testing level leads to lower restrictions
- Strict test order is not acceptable at Unit level
- … but might be OK at Integration level
JUnit5 Framework
- Annotation driven (mostly at method level)
@Test used to mark test methods@BeforeEach/@AfterEach for per test setup/teardown@BeforeAll/@AfterAll for shared setup/teardown
- Must be
static (once per all tests in single class)
- Highly extendable
Assertions in JUnit5
- Default JUni5 Assertions API
- Assertions based on matchers (e.g. Hamcrest)
- Fluent assertion libraries (e.g. AssertJ)
Component Dependencies
Car > Engine > Cylinder
- Design for loose coupling and IoC
- Control your objects’ dependencies
- Use testing implementations
Test Doubles
“Looks real but actually isn’t!”
- Stub double
- Returns predefined values
- Spy double
- Fake double
- Fully functional implementation
- … not suitable for production






